What is GISS?
Download book in PDF, 5Mb3.11 Ensuring the sustainability of the country’s governance during the crisis period of the outbreak of hostilities
Existing in the Russian Federation, in general, as in all other countries, information and telecommunication networks rely on the well-known routes for laying fiber-optic cable lines (underwater, underground, on high-voltage power lines and oil pipelines) and switching centers for their information flows, which at the beginning of the war with high probability will (can be) disabled physically, without considering options for cyber-attacks.
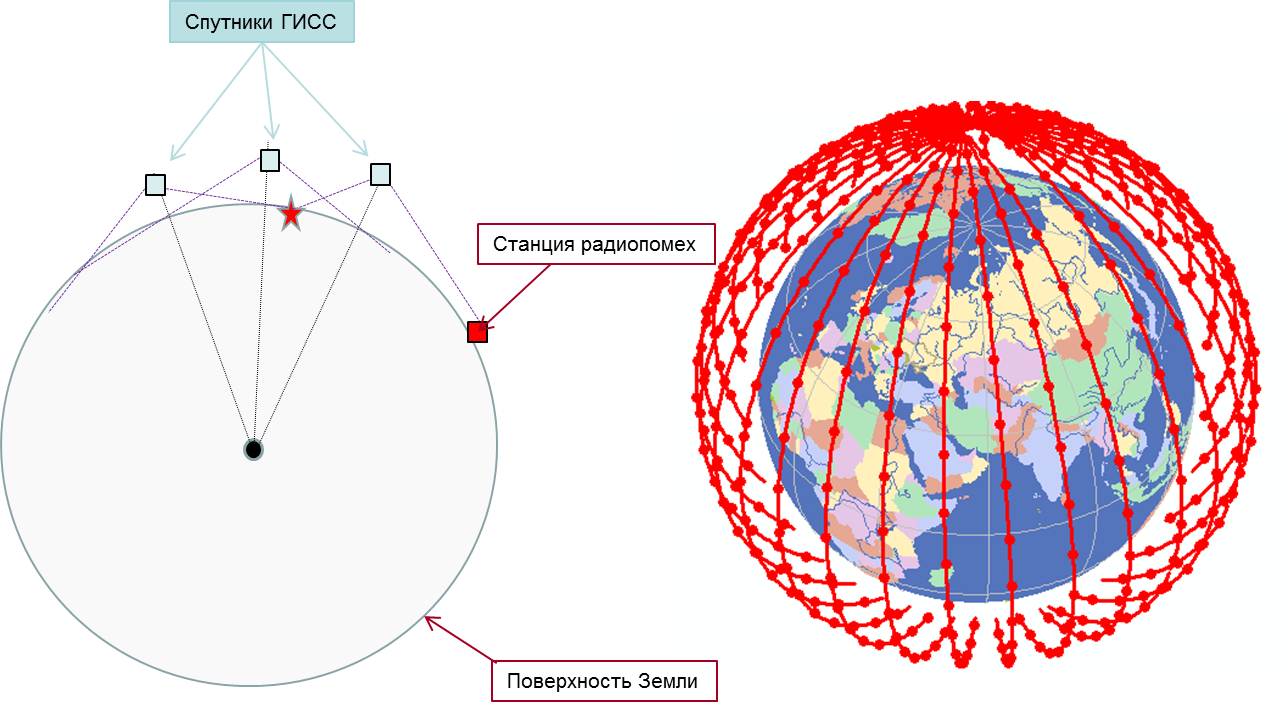
The created satellite communication channels, as it were, of anti-jamming control of the armed forces (AF), in fact, are fundamentally suppressed by the enemy, the whole point is in the level of interference power directed towards the communication satellite and the location of the jamming station. It is based on the physics of solving the problem of each of the opposing sides – communication and radio jamming suppression, which does not imply a guaranteed solution to the communication problem. This applies equally to both the military communications system of the Russian Federation and the military satellite communications system of the United States and NATO countries, which can be suppressed in principle, only large antenna sizes and the radiation power of a radio jamming station located in their service areas are required.
The proposed GISS, even without the use of anti-jamming signal-code structures, is practically not suppressed and will provide control of the country and its armed forces for the participants in its implementation during the period of hostilities with any international association of opponents. In this case, the bandwidth of communication channels between any regions will be at least 2÷4 Gbps, the information flows in which can be distributed within the region.
The stability of the GISS is determined by the principle of constructing an orbital constellation for solving the problem of active-passive radar monitoring of the earth’s space. At any point on the Earth, lying on the other side of the conventional front, where the radio jamming station is located, in the control center’s visibility zone there are at least two more L-band satellites and two X-band satellites, the reception area of which does not lie in the visibility zone of the radio interference station. Thus, the access of any terminal in the country and aircraft management system to the inter-satellite optical transport network is preserved, through which IP packets will be delivered to the required receiving point (see Fig. 3.27).
A special hardware and software processing complex as part of the Regional ground complex for receiving and processing signals from the attacked country, in less than one minute, can determine the location of the radio suppression station with an accuracy of 10 ÷ 15 meters, which, with good control organization, will be destroyed by the missile in a few minutes.
On the downlink, interference can only be placed in the line of sight of the receiving terminal (25–30 km), the source of which is determined and destroyed by its operational tactical (tactical) means.
From the point of view of resolving the problem of governing the country, one can also make an assessment of the Starlink project of the SpaceX company by Elon Musk. Yes, this project solves the problem of managing the forces of the expeditionary corps and all branches of the armed forces on the territory of a country with a destroyed information and telecommunications infrastructure. The idea of providing humanity with broadband Internet access is good, especially about the UK’s concern for the people of Nepal, which Mount Everest has blocked the visibility of geostationary communication satellites, as was one of the goals (legends) of the OneWeb project. Moreover, the economics of the commercial recoupment of the costs of creating such a Starlink orbital constellation, maintaining the operation, the cost of terminals and the price for the communication services provided to a wide range of civilian users are somehow not clear enough, perhaps only for me.
I remember that in the early 70s of the last century, there was also an “enthusiast” Howard Hughes, he was “tired of doing aviation”, he decided to start deepsea drilling of the ocean floor for mining. He built the ship “Glomar Explorer” and drilled the bottom in the Pacific Ocean, the second ship “Glomar Challenger” for research and taking eyes off the main target drilled the bottom in the Bermuda Triangle. Then it turned out that this project was funded from secret US funds for the Azorian project to raise the Soviet Union’s K-129 submarine.
Mr. Elon Musk, even if you were not appointed as another “enthusiast”, that is, a proposal that attracts even more financial resources, it will allow, in the interests of the entire world community, to create a GISS, which will solve many problems in the interests of all countries. Including the prevention of a sudden gratuitous nuclear missile attack, not to mention a simpler solution to the problem of communication and broadband Internet access for underdeveloped regions.
It is better to put into operation such a GISS, containing a constellation of only 288 (576) large satellites in 12 (24) orbital planes, than to litter our common space according to your plans from 1200 to 12000 small satellites, in the interests of a limited group of countries.